- The Limits of RAG and Single-Agent GenAI
- What Are GenAI Agents and Why Do They Matter?
- Inside Multi-Agent Collaboration: Real-World Application in App Modernization</a/>
- Benefits of Multi-Agent GenAI in Software Engineering
- 1. Specialization Boosts Depth
- 2. Iterative Feedback Improves Quality
- 3. Parallel Execution Saves Time
- 4. Scalability Across Projects
- 5. Closer to Human Team Dynamics
- Challenges and Risks to Watch for with GenAI in Software Development
- The Promising Software Renders with Multi-Agent AI Systems!
AI is evolving from helpful tools to decision-making collaborators, and nowhere is that shift more visible than in software engineering. Today, large language models (LLMs) can help with code suggestions, documentation, and bug fixes. But for complex, multi-step tasks like end-to-end app modernization, a single GenAI agent often falls short.
The next step is Multi-Agent GenAI: a system where several LLM-powered agents work together like a human team, each with a specific role. Such a collaborative setup is changing how we build, test, and maintain software faster, more accurately, and with less human effort.
In this blog, we explain how multi-agent AI works, where it’s used, its main benefits, and the risks to keep in mind as it becomes part of future development releases.
The Limits of RAG and Single-Agent GenAI
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has improved LLM performance by giving models access to external data. With tools like vector databases, GenAI can now retrieve relevant content before generating responses, resulting in more accurate and useful answers. LLM Chains take this further by combining multiple tasks in sequence, enabling the model to perform slightly more complex actions.
However, these setups still work best for tasks that are linear and clearly defined. They struggle when the problem involves understanding complex logic, long dependencies, or creative decision-making. For example, building a full-stack app or refactoring legacy systems involves planning, iteration, and domain knowledge that a single model or chain can’t fully handle.
Software engineering requires specialized reasoning that something one general-purpose agent may lack. Multi-agent systems bridge the gap.
What Are GenAI Agents and Why Do They Matter?
GenAI Agents are LLM-powered units designed to act with autonomy. They’re not just responding to prompts—they can initiate tasks, reflect on feedback, interact with tools, and manage memory. This makes them suitable for solving real-world challenges.
What makes these agents special is their ability to act with intent. A GenAI Agent can:
- Break down a high-level goal into smaller actionable steps
- Interact with APIs, files, or databases
- Use memory to store and recall past results
- Review its own work and improve over time
They are built to mimic human problem-solving by incorporating reasoning, self-correction, and task-specific learning. While one agent can be effective, combining many of them is where things get interesting.
Inside Multi-Agent Collaboration: Real-World Application in App Modernization
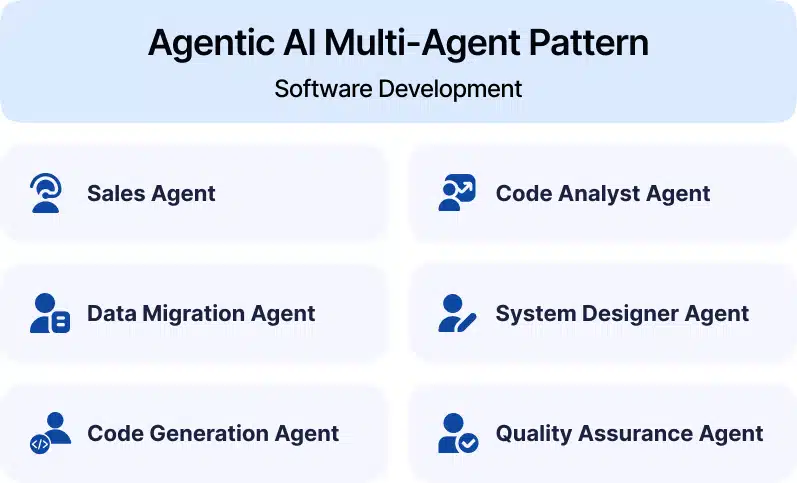
A practical example of multi-agent collaboration is app modernization. Many organizations still operate on outdated tech stacks, say, a mix of Java code and SQL stored procedures.
Migrating to modern frameworks like Spring Boot with MongoDB isn’t simple. You can’t just convert the code—you need to understand the business logic, redesign the architecture, rewrite integrations, and update data flows.
Using a multi-agent GenAI system, this process becomes much easier:
- A Code Analyst Agent reviews legacy Java to extract core business logic.
- A Data Migration Agent converts SQL queries to MongoDB-compatible formats.
- A System Designer Agent drafts a scalable backend architecture.
- A Code Generation Agent writes the actual code in the modern stack.
- A QA Agent creates and runs tests.
- A Documentation Agent explains all changes in human-readable format.
Platforms like Peer.AI use such orchestration to automate the full software lifecycle. With the right configuration, an entire app migration project that would take weeks can be done in a fraction of the time with better accuracy and less manual effort.
Benefits of Multi-Agent GenAI in Software Engineering
The benefits of Multi Agent Generative AI systems are as follows:
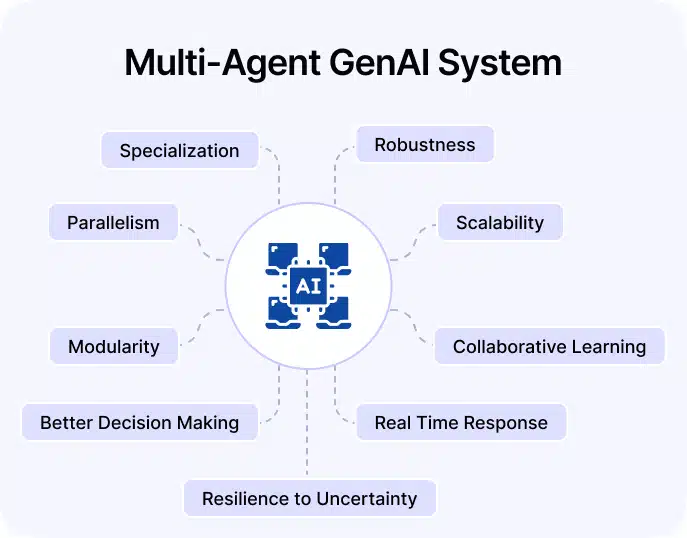
1. Specialization Boosts Depth
Each agent is trained or configured to handle a specific task be it writing code, testing logic, or managing infrastructure. By narrowing their focus, agents produce more relevant, reliable, and deeply contextual results.
2. Iterative Feedback Improves Quality
Instead of a single pass, agents check each other’s outputs. A QA agent can find bugs in the developer’s code, and the developer agent can fix them based on suggestions. This loop improves overall code quality without requiring constant human review.
3. Parallel Execution Saves Time
Unlike linear pipelines, multi-agent systems can work simultaneously on different parts of the project. One agent generates documentation while another writes test cases, reducing the total time from start to finish.
4. Scalability Across Projects
Once an agent or agent team is built, it can be reused across different projects or clients. Such a scalability reduces ramp-up time and allows companies to deliver consistent output across use cases.
5. Closer to Human Team Dynamics
By mimicking the way real teams work through roles, communication, and division of labor, multi-agent systems better adapt to real-world challenges. This makes them more flexible and suitable for complex software tasks.
Challenges and Risks to Watch for with GenAI in Software Development
- Coordination Overhead
More agents mean more complexity. If orchestration isn’t handled well, outputs can clash or get stuck in loops. Designing clear handoffs between agents is crucial. - Increased Compute Load
Running multiple agents in parallel uses more computing power. Without optimization, this can lead to higher cloud bills and latency issues. - Error and Bias Propagation
One flawed output can affect all downstream agents. For example, if a requirements agent misunderstands a feature, the developer agent may write the wrong code, and the tester may miss the problem altogether. - Lack of Explainability
It can be difficult to understand how and why certain decisions were made, especially when agents generate outputs autonomously. Logs, version control, and model reasoning paths must be tracked to ensure transparency. - Security and Governance
Autonomous agents making decisions in live codebases or handling sensitive data can pose security and compliance risks. Human oversight and approval workflows must be part of the loop.
The Promising Software Renders with Multi-Agent AI Systems!
As the tools improve and orchestration becomes smoother, multi-agent GenAI will move from experimental to mainstream in software development. These systems will help automate larger chunks of the software lifecycle from design to deployment while letting humans focus on planning, innovation, and strategy.
We’re already seeing early use cases where this setup transforms workflows. In the future, IDEs might come pre-configured with agent teams, or cloud platforms might offer agent orchestration as a service.
That said, humans won’t be replaced. Developers will become more like directors, guiding, reviewing, and fine-tuning agent collaboration. Creative thinking, ethical oversight, and architectural judgment will still be human strengths.
The key to success will be designing workflows that blend automation and responsibility. Explainability, observability, and governance will be vital. But for companies looking to scale and move faster, multi-agent GenAI is emerging as a powerful tool in the next era of software engineering.
Ready to explore how multi-agent GenAI can transform your development process?
Stay tuned as Helius Work keeps you updated into this exciting space. Engineering teams can aim to boost productivity, reduce technical debt, and scale fast.